#Product Trends
APS construction method
Advanced Japanese conventional frame construction method
"Modern Japanese Nails, Revolutionary Joining Hardware"
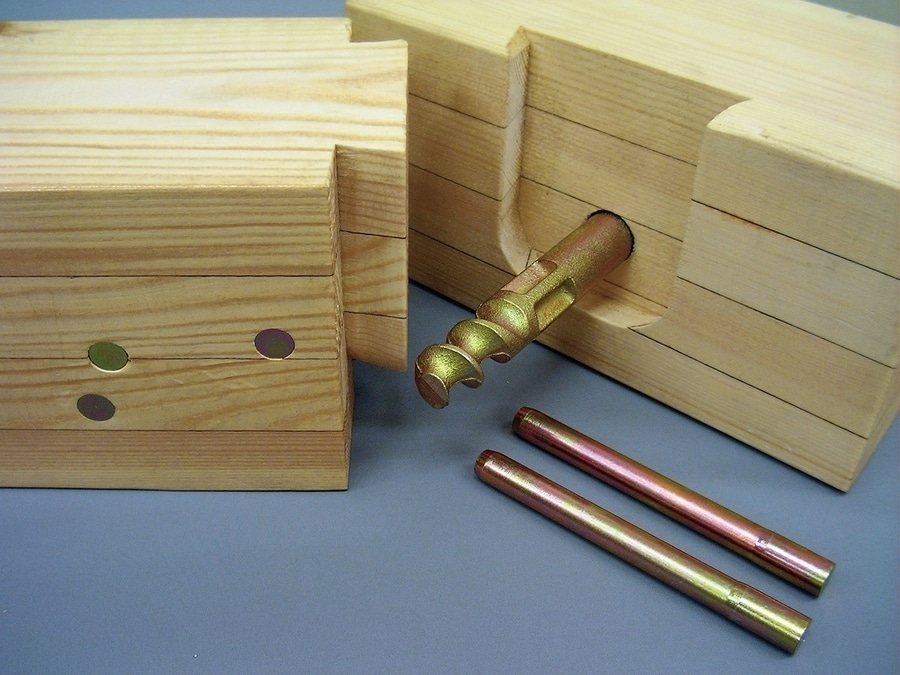
The Modern Japanese Nail. Apple Pin System (APS construction method) is a further evolution of the traditional Japanese construction method "Conventional Post-Beam Construction Method".
By placing the apple pins inside the columns and beams, the beauty of wooden construction can be expressed along with enhanced earthquake resistance.
In order to realise safe, high-quality wooden houses, and for the sake of new possibilities for wooden houses, the know-how gained through experience with the Tokorozawa-city Gymnasium, the world's largest wooden gymnasium, is being utilised for the further evolution of wooden houses.
"Evolutionary Function: Significantly Improved Housing Quality"
Techniques that utilise the expression of the beauty of the grain of traditional Japanese wooden construction and the wisdom of carpenters have made it possible to create beautiful finishes with no visible hardware.
Furthermore, compared to other construction methods, it is fireproof and airtight, and since bolts and nuts are not used in the basic structure, rattling is less likely to occur, and pulling and tightening torque management is easy.
Compared to conventional construction methods, there are fewer cross-sectional defects, which improves the strength of timber joints and provides sufficient durability.
"Highly Cost-Effective and Environmentally Friendly"
The Apple Pin System (APS construction method) can be introduced by making slight customisations to existing conventional construction method pre-cut factory lines.
It has also been developed on the basis of conventional dovetail processing.
It is less uncomfortable for craftsmen who are processing for the first time and improves workability.
Furthermore, the Apple Pin System (APS construction method) has no protruding metalwork when it leaves the factory.
This means that loads are less bulky and transport costs are comparable to conventional construction methods, leading to lower CO2 emissions from transport.